Librarian Futures Part IV: AI Is in Student Workflows—Is Your Library?
Posted July 25th 2025
Posted July 25th 2025
As AI becomes a staple in academic workflows, students are embracing tools like ChatGPT, Claude and Microsoft Copilot for tasks such as summarizing resources, drafting essays and exam preparation. But while generative AI is transforming how students learn, it’s also introducing new pressures and uncertainty—especially around academic integrity, mental wellbeing, and finding trustworthy guidance.
The latest Librarian Futures Part IV report, Librarian Leadership on the AI Frontier, confirms what many librarians already suspect. Most students feel overwhelmed (57% report feeling this way often or very often), but few are turning to the library for help. Only 17% of students would turn to a librarian for AI guidance. Even fewer (8%) report having received guidance from librarians on how to use AI in their studies. How can academic librarians play a vital role in guiding students and researchers with the responsible use of AI and embed the library into emerging AI workflows?

Librarian Futures Part IV, Librarian Leadership on the AI Frontier, draws on global surveys of 1000 students and 300 librarians
Discover the ways that institutions have used Lean Library, a trusted tool which streamlines access to library resources, to bridge this critical gap and bring the expertise, support, and services of the academic library directly into students’ workflows. Here’s how:
The latest Librarian Futures report found that students use multiple sites to find research in addition to the library website; 67% use Google, 55% use ChatGPT and 44% use Google Scholar. Instead of expecting students to seek out the library for help, Lean Library meets them where they are with Assist Messages (personalized messages from the library for users). For example, Lean Library can deliver a message through the pop-up with citation advice when students are browsing ChatGPT, or link to the library’s AI policy when students start their research on AI websites.
One library has deployed Assist Messages on multiple AI platforms including Perplexity, ChatGPT, Claude and Microsoft Copilot to direct students to the library guidance and policy around using these tools responsibly and ethically.
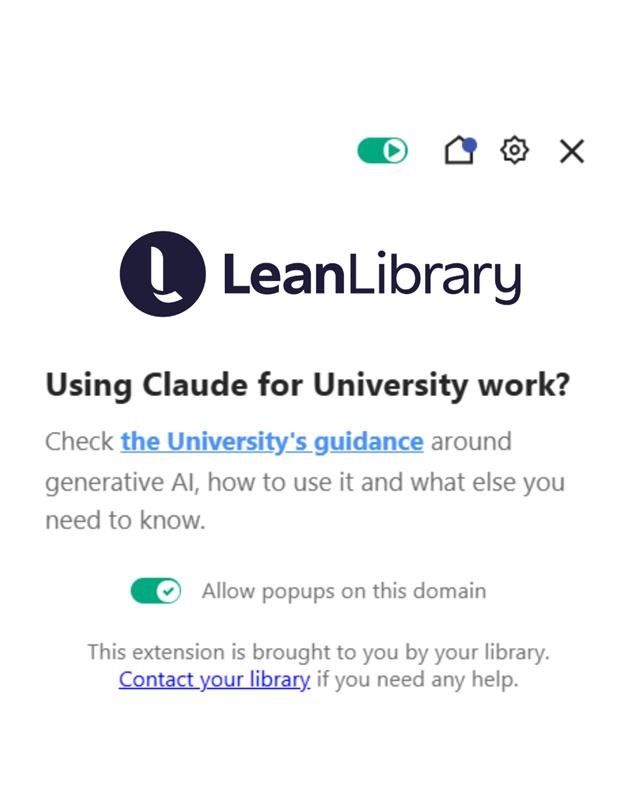
An example of an Assist Message which directs students to Claude guidance
Many students want help using AI responsibly but don’t know where to turn. Librarian Futures Part IV shows students are far more likely to trust an AI tool if it’s recommended by their library, yet they rarely receive that guidance.
One way for librarians to teach students how to use AI tools effectively is by directing them to free, trusted courses on AI digital literacy. For example, the Sage Campus and Lean Library integration surfaces the short online course, The Art of ChatGPT Interactions, to students and researchers when they are in locations within the OpenAI.com domain. The course was designed by AI expert Dr Leo. S Lo, Dean of the College of University Libraries & Learning Sciences at the University of New Mexico.
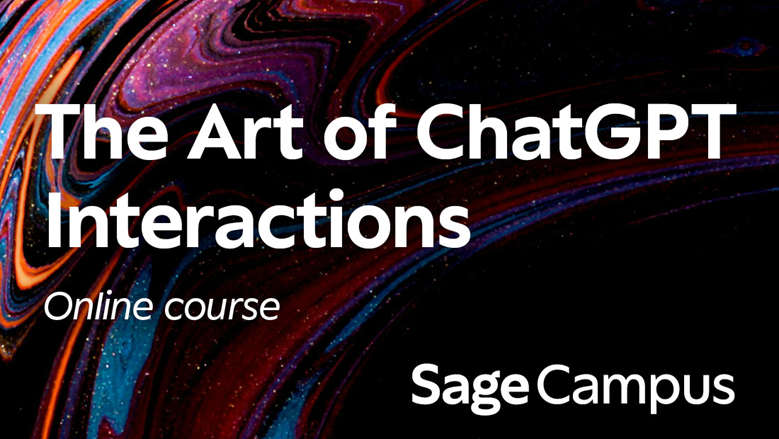
The Art of ChatGPT Interactions online short course, designed by AI expert Dr Leo. S Lo
This means students can learn about using AI effectively, improve their prompt engineering and achieve outcomes for their studies and research, without their workflow being interrupted. The library recommending free, trusted courses to students, created by librarians, mitigates the risk of the students picking up incorrect guidance as there are multiple AI courses available. This aims to reduce student stress and improve AI and research outcomes, whilst positioning the library as the go-to source for AI guidance.
Find out more about the Sage Campus AI course and how University of Phoenix have combined Lean Library‘s iFraming technology with Springshare’s LibGuides integration.
A fascinating finding from the report is that 27% of students wouldn’t look to anyone at their institution for AI guidance—more than those who would turn to a librarian (17%). Libraries have written multiple AI guides and resources for students, but how can they make sure they’re being shown to students at the point-of-need and not hidden on a library website?
With Lean Library, Library Guides or LibGuides (via Lean Library’s integration with Springshare), onboarding and instructional materials can be deployed on any academic resource or website to reach users right when they need it. This means the guidance is visible on sites such as Google Scholar, publisher websites, or even ChatGPT, rather than students searching for it.
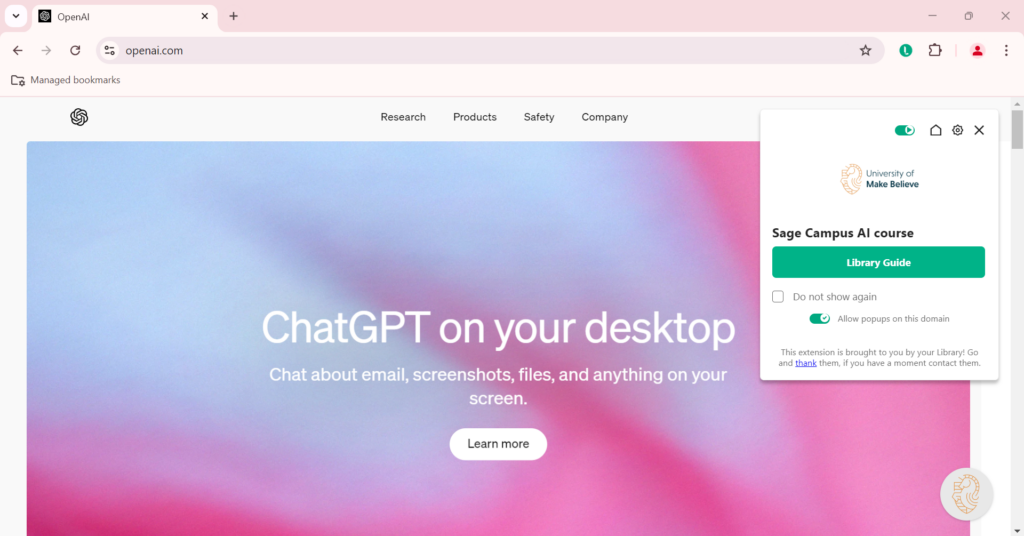
An example of Lean Library surfacing a Library Guide directing students to the Sage Campus AI course
Check out how Utah State University have embedded LibGuides in student workflows, increasing usage of a LibGuide by 450%.
Librarian Futures Part IV highlights that one of the few areas where students do turn to librarians is for getting access to resources—something Lean Library excels at. By removing barriers to access and improving discoverability of legitimate, library-provided materials, Lean Library helps students spend less time hitting paywalls and more time doing meaningful work.
Streamlining access has many positive benefits including reducing academic stress, especially for students juggling deadlines and unclear institutional AI policies. University of Hertfordshire adopted Lean Library to make it easier for students to find and access both library-subscribed materials and Open Access resources.
“There’s the risk if you don’t provide easy routes to access things legally, then potentially people may decide to do things via routes that increase risk to the institution—things that open you up to a cybersecurity risk. It was also part of a risk management strategy: let’s make this as easy as possible so they don’t try and do something that opens their own device to risk or an institutional device.”
Rebecca Scott, Project Manager, University of Hertfordshire
Read more about University of Hertfordshire’s case study.
Finally, librarians can feel empowered to personalize their presence with the Lean Library Library Chat (LibChat) feature. The LibChat integration allows librarians to deploy their live chat service to patrons. This can be very helpful for students when they face a challenging situation and want targeted support without having to go to the library’s contact page to find it.
As 60% of students said they would rather hear from the library only ‘when and where they need it’, and 53% of GenZers say they feel more comfortable communicating online than in person, this kind of humanized, live-action support can reestablish the librarian as a trusted partner in learning.
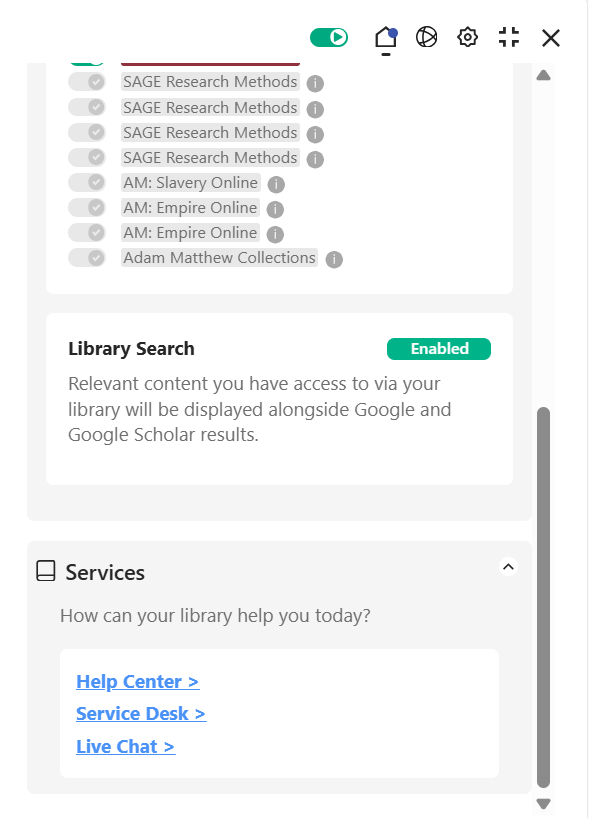
An example of a Lean Library pop-up showing students directed to Library Chat, Services Desk and Help Centre
The Librarian Futures Part IV report makes it clear: students trust their librarians, but they don’t always think to turn to them. Lean Library helps change that. By embedding the library where it’s needed most—in the student workflow and on AI sites students use to begin their research—Lean Library not only supports academic success but also reduces stress and builds confidence in the AI age.
Let’s meet students where they are and bring AI guidance to them directly in their workflow, rather than have students look for AI access and support elsewhere.
“It is important to balance the benefits of AI with responsible usage, both in our professional practice and in effectively guiding students through this rapidly changing landscape. By promoting digital literacy, librarians play a key role in helping students effectively use and assess AI-generated content in their academic work and beyond.”
PJ Purchase, University Librarian and Director of University Library, University of Phoenix
Find out more about Lean Library.
If you’d like to hear more or receive a product demo, get in touch.